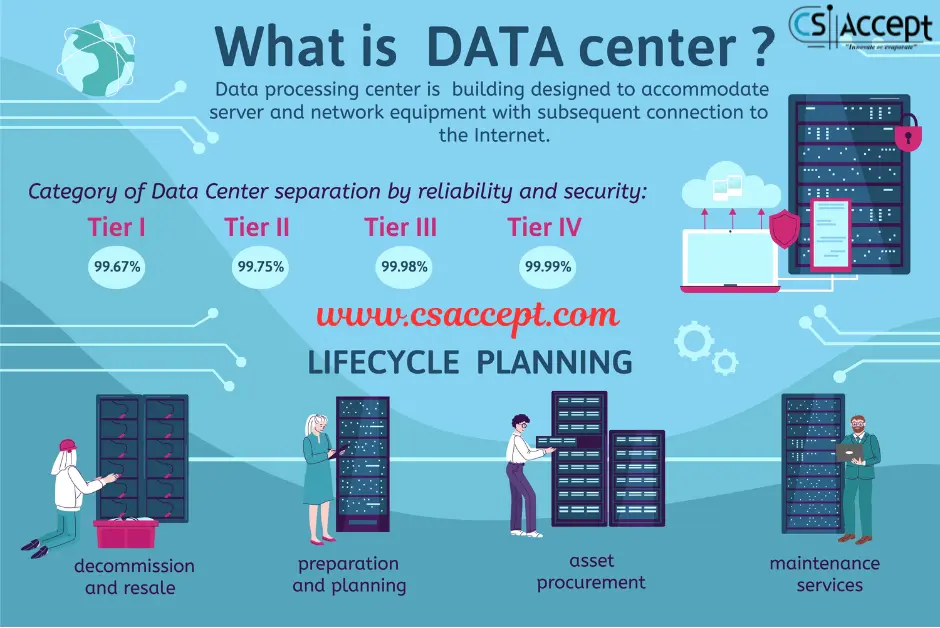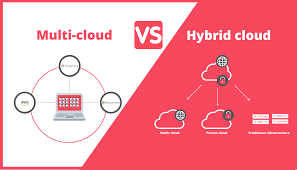
1. Definition
Multicloud:
- Multicloud is the use of multiple cloud services from different cloud providers simultaneously. It involves running workloads across two or more public cloud environments.
- The key here is diversity: different clouds may be used for different services or applications to avoid vendor lock-in, optimize cost, or leverage unique features.
Hybrid Cloud:
- Hybrid cloud combines private (on-premises or private cloud) infrastructure with public cloud resources, allowing data and applications to be shared between them.
- It integrates both environments, providing more flexibility, data control, and scalability.
2. Key Differences
| Feature | Multicloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Types | Multiple public clouds from different vendors | Combination of private cloud and public cloud |
| Purpose | Avoid vendor lock-in, optimize best-of-breed cloud services | Combine security/control of private cloud with scalability of public cloud |
| Integration | Clouds are mostly independent, minimal direct integration | Tight integration and orchestration between private and public clouds |
| Data Location | Data and apps reside in multiple public clouds | Data can move between private and public clouds |
| Use Case Focus | Using best services from various providers | Seamless operation of workloads across private and public infrastructures |
| Management Complexity | Higher due to managing multiple providers | Complex, but typically fewer providers involved |
3. Advantages
Multicloud:
- Avoid vendor lock-in by not relying on a single cloud provider.
- Flexibility to choose best services for specific tasks (e.g., AI services from AWS, analytics from Google Cloud).
- Increased redundancy and resilience by distributing workloads across clouds.
- Ability to negotiate better pricing by leveraging multiple providers.
Hybrid Cloud:
- Better control over sensitive data by keeping it on-premises/private cloud.
- Ability to scale using public cloud resources during peak demand.
- Compliance with regulations that restrict data location.
- Seamless workload portability between private and public environments.
4. Examples
Multicloud Example:
- A company uses Amazon Web Services (AWS) for its primary web hosting and database services.
- It uses Microsoft Azure for its AI and machine learning workloads.
- It uses Google Cloud Platform (GCP) for big data analytics.
- Each cloud runs independently, managed by separate teams, optimizing cost and capabilities for different tasks.
Hybrid Cloud Example:
- A healthcare organization keeps patient records on a private cloud to meet HIPAA compliance.
- They run their billing and appointment scheduling systems on a public cloud (e.g., AWS) for scalability.
- The two environments are integrated so the billing system can securely access patient info when necessary.
- During a pandemic surge, the organization scales public cloud compute resources to handle increased demand while sensitive patient data remains on-premises.
5. Summary Table
| Aspect | Multicloud | Hybrid Cloud |
|---|---|---|
| Cloud Environment | Multiple public clouds | Private + Public cloud |
| Integration | Low to moderate | High integration |
| Data Control | Spread across providers | Control over sensitive data |
| Use Cases | Best-of-breed services, redundancy | Compliance, data control, scalability |
| Complexity | High management of multiple clouds | Complex integration but fewer clouds |
| Example Providers | AWS, Azure, GCP used simultaneously | Private cloud + AWS or Azure |