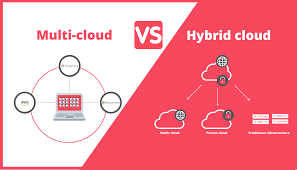
Multicloud vs Hybrid Cloud with example
1. Definition Multicloud: Hybrid Cloud: 2. Key Differences Feature Multicloud Hybrid Cloud Cloud Types Multiple public clouds from different vendors Combination of private cloud and public cloud Purpose Avoid vendor…